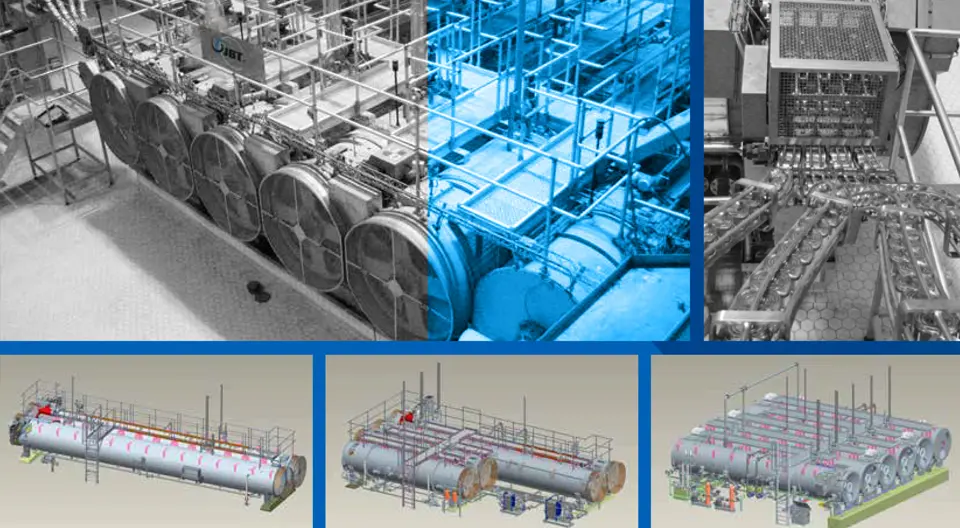
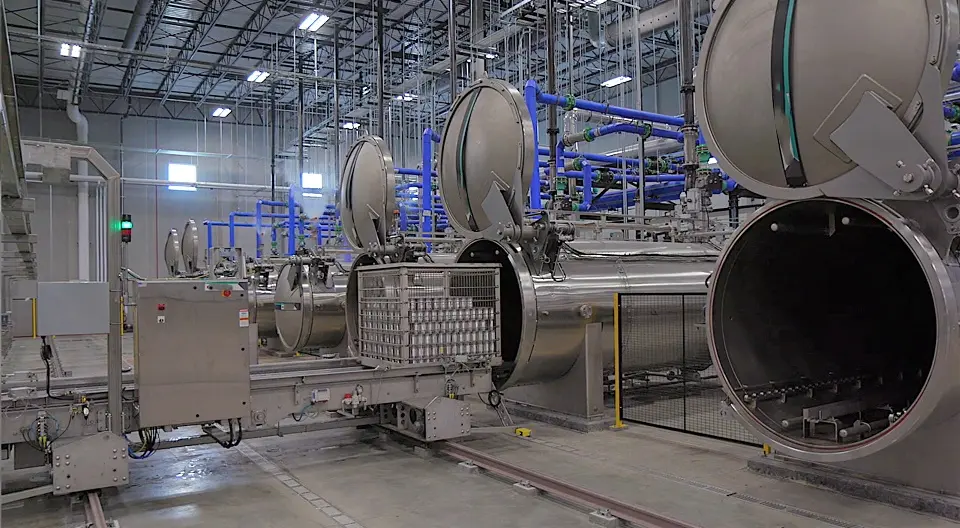
Selecting the Best Retorting System
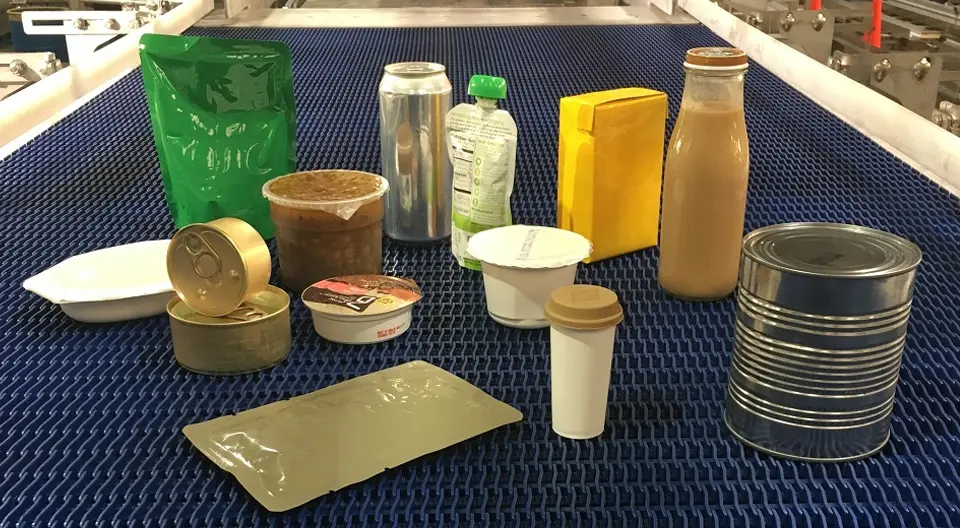
Choosing the Right Retorting System for Your Containers and Products Retorting systems play a pivotal role in the food packaging industry, particularly when it comes to ensuring the safety and longevity of various food products. These systems utilize heat to sterilize containers filled with food, effectively killing pathogens and microorganisms that could compromise food safety. The process involves placing filled and sealed containers in an autoclave or a pressure cooker-like environment, where they are subjected to controlled temperatures and pressures. This critical step not only helps in maintaining the edibility of food but also significantly enhances its shelf stability. As the demand for convenience and long shelf life increases among consumers, the evolution of retorting systems has become intertwined with packaging innovations. Modern retorting systems are engineered not only for efficiency but also for versatility, accommodating a wide array of container types and materials. From glass jars to metal cans and flexible pouches, these systems are designed to provide optimal sterilization without compromising the integrity of the packaging. Moreover, advancements in technology have led to more automated processes, allowing for accurate monitoring and control of temperature and time, thus ensuring consistent results. Furthermore, the adoption of retorting systems is vital for extending the shelf life of food products, which contributes to reduced food waste and greater food availability. In today’s global market, where food products often travel long distances, utilizing effective retorting processes ensures that consumers receive safe, high-quality food. The importance of retorting systems cannot be understated, as they not only safeguard public health but also align with sustainable practices by maximizing the usable life of food products. Through these systems, manufacturers can deliver reliable and safe food options to consumers while adapting to ever-evolving packaging technologies. The Evolution of Shelf-Stable Food Packaging Over the past two decades, the landscape of shelf-stable food packaging has undergone remarkable advancements. Traditionally, consumers relied on metal cans and glass jars to store and preserve food. These packaging types were effective in maintaining food safety and extending shelf life but had limitations in terms of weight, fragility, and recyclability. As the demand for convenience and sustainability grew, the food packaging industry began to innovate, leading to the emergence of modern packaging solutions. The introduction of polymeric materials marked a significant turning point in shelf-stable packaging. These flexible materials proved to be lightweight and less prone to breakage compared to their metal and glass counterparts. Polymeric pouches, for example, offer an excellent barrier against oxygen and moisture, ensuring the freshness and longevity of food products. Additionally, these pouches can be designed in various shapes and sizes, catering to different consumer needs, and making them ideal for a vast range of food items. Composite packaging has also gained attention as a viable solution for shelf-stable foods. These materials integrate the benefits of both rigid and flexible packaging, providing durability coupled with lightweight features. Composite bowls, cups, and trays are increasingly popular for ready-to-eat meals, offering not only functional advantages but also appealing aesthetics that attract consumers. The use of these innovative packaging options facilitates ease of storage and transportation while also maintaining food quality. Furthermore, advancements in technology have led to improved manufacturing processes that enhance the sustainability of packaging materials. Many manufacturers are exploring biodegradable and recyclable options to minimize their environmental impact while ensuring that shelf-stable food products remain safe and appealing to consumers. As the food industry continues to evolve, the push towards more innovative, sustainable, and consumer-friendly packaging solutions is likely to persist, shaping the future of shelf-stable food packaging. Overview of Advanced Retorting Technologies In recent years, the food packaging industry has witnessed significant advancements in retorting technologies, largely driven by the need for enhanced food safety, quality preservation, and efficiency. Advanced retorting systems have emerged as sophisticated solutions to meet these evolving demands. Among these innovations are complex overpressure sterilizers, which play a crucial role in ensuring that packaged products are free from microbial contamination while retaining their nutritional and sensory properties. Advancements in retorting technology have allowed for greater control over the sterilization process. By employing precise temperature profiles and monitoring systems, operators can ensure optimal conditions for each specific type of product being processed. This level of customization is particularly beneficial for manufacturers aiming to produce a diverse range of items, including sauces, soups, and ready-to-eat meals, all of which may require tailored processing parameters to preserve their unique qualities. The various retort processing methods includes: Water Immersion Processing Water immersion is a commonly used retort processing method, where water is first heated in a storage vessel and then transferred into the processing vessel for thermal processing. The container is typically fully immersed in water during processing, with overpressure created by blowing air or steam for improved heat transfer patterns. But, in certain situations, such as with half‐immersion, where the containers are only partially immersed in water (less than half). This will be beneficial for high rotational speeds, as the cage creates less turbulence. Water is recirculated by using a circulation pump during the heating process to ensure uniform heat distribution throughout the retort. It is to be noted that poor circulation can result in insufficient heat transfer. Controlling the float of packages can be a challenge, and containers like pouches and trays have often impeded this process, increasing basket manufacturing costs and reducing adaptability. Half‐immersion method is when the the processing vessel is half‐filled with water such that part of the rotation occurs in and out of the water. This method is beneficial for higher rotational speeds because the basket creates less turbulence. Water Cascade Processing The water cascade retort, also known as a water shower retort system, operates by showering process water over the retort baskets. Process water is drawn from the retort’s base, indirectly heated via an external heat exchanger, and then redistributed at the retort’s top. This water flows across a perforated distribution plate, cascading down onto the product baskets. The plate’s dimensions typically match the combined length of a full load